NeoEMF : A Multi-database Model Persistence Framework.
The figure below describes the integration of NeoEMF in the Eclipse-based EMF ecosystem, the most popular modeling framework nowadays. Modelers typically access a model using Model-based Tools, which provide high-level modeling features such as a graphical interface, interactive console, or query editor. These features internally rely on EMF's Model Access API to navigate models, perform CRUD operations, check constraints, etc. At its core, EMF delegates the operations to a persistence manager using its Persistence API, which is in charge of the (de)serialization of the model. The NeoEMF core component is defined at this level, and can be registered as a persistence manager for EMF, replacing, for instance, the default XMI persistence manager. This design makes NeoEMF both transparent to the client-application and EMF itself, that simply delegates the calls without taking care of the actual storage.
Once the NeoEMF core component has received the request of the modeling operation to perform, it forwards the operation to the appropriate database driver (MapDB, Blueprints, or HBase), which is in charge of handling the low-level representation of the model. These connectors translate modeling operations into Backend API calls, store the results, and reify database records into EMF EObjects when needed. NeoEMF also embeds a set of default caching strategies that are used to improve performance of client applications, and can be configured transparently at the EMF API level.
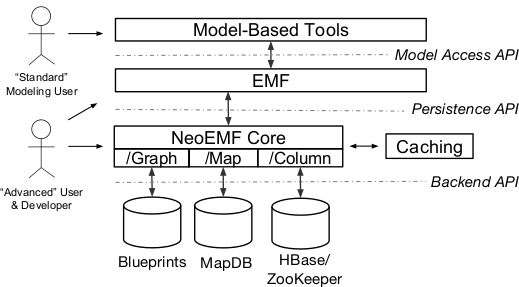
Each backend is provided in a dedicated Eclipse plugin. you can navigate through the documentation to have a complete overview of backend-specific classes and how they interact with the core component. NeoEMF provides 4 database adapters for now:
- Blueprints - TinkerGraph: the default graph database embedded in Blueprints
- Blueprints - Neo4j: Neo4j graph database under the Blueprints API
- MapDB: an in-memory/on-disk Map database
- HBase: a distributed Column database
Sources are available on GitHub. Further informations can be found on NeoEMF website.